Con Drush podemos crear la estructura principal del módulo, por ejemplo el archivo info.yml y el archivo .module. Pero también podrá crear otros archivos según las opciones que escogamos, como (librerías, archivo de instalación, permisos, rutas, servicios, etc).
Lo primero que debemos hacer es instalar drush en nuestro proyecto con:
$ composer require drush/drushLuego Drush se instalará y será ejecutable desde ./vendor/bin/drush, por lo tanto debemos colocarnos a la altura de la carpeta vendor de nuestro proyecto para ejecutar los comandos que veremos a continuación.
1. Para crear un módulo con drush debemos usar drush generate, por lo que primero conoceremos las opciones de dicho comando ejecutando:
$ ./vendor/bin/drush generateEsto nos mostrará una lista de opciones con sus respectivas explicaciones de lo que hace cada una:
Drupal Code Generator 3.0.0
Run `drush generate [command]` and answer a few questions in order to write starter code to your project.
Available commands:
_global:
composer (composer.json) Generates a composer.json file
controller Generates a controller
field Generates a field
hook Generates a hook
install-file Generates an install file
javascript Generates Drupal JavaScript file
layout Generates a layout
module Generates Drupal module
phpstorm-meta Generates PhpStorm metadata
render-element Generates Drupal render element
service-provider Generates a service provider
drush:
drush:alias-file (daf) Generates a Drush site alias file.
drush:command-file (dcf) Generates a Drush command file.
drush:generator (generator) Generates Drush generator
drush:symfony-command (symfony-command) Generates Symfony console command
entity:
entity:bundle-class (bundle-class) Generate a bundle class for a content entity.
entity:configuration (config-entity) Generates configuration entity
entity:content (content-entity) Generates content entity
form:
form:config (config-form) Generates a configuration form
form:confirm (confirm-form) Generates a confirmation form
form:simple (form) Generates simple form
misc:
misc:apache-virtual-host (apache-virtual-host) Generates an Apache site configuration file
misc:nginx-virtual-host (nginx-virtual-host) Generates an Nginx site configuration file
plugin:
plugin:action (action) Generates action plugin
plugin:block (block) Generates block plugin
plugin:ckeditor (ckeditor, ckeditor-plugin) Generates CKEditor plugin
plugin:condition (condition) Generates condition plugin
plugin:constraint (constraint) Generates constraint plugin
plugin:entity-reference-selection (entity-reference-selection) Generates entity reference selection plugin
plugin:field:formatter (field-formatter) Generates field formatter plugin
plugin:field:type (field-type) Generates field type plugin
plugin:field:widget (field-widget) Generates field widget plugin
plugin:filter (filter) Generates filter plugin
plugin:manager Generates plugin manager
plugin:menu-link (menu-link) Generates menu-link plugin
plugin:migrate:destination (migrate-destination) Generates migrate destination plugin
plugin:migrate:process (migrate-process) Generates migrate process plugin
plugin:migrate:source (migrate-source) Generates migrate source plugin
plugin:queue-worker (queue-worker) Generates queue worker plugin
plugin:rest-resource (rest-resource) Generates rest resource plugin
plugin:views:argument-default (views-argument-default) Generates views default argument plugin
plugin:views:field (views-field) Generates views field plugin
plugin:views:style (views-style) Generates views style plugin
service:
service:access-checker (access-checker) Generates an access checker service
service:breadcrumb-builder (breadcrumb-builder) Generates a breadcrumb builder service
service:cache-context (cache-context) Generates a cache context service
service:custom (custom-service) Generates a custom Drupal service
service:event-subscriber (event-subscriber) Generates an event subscriber
service:logger (logger) Generates a logger service
service:middleware (middleware) Generates a middleware
service:param-converter (param-converter) Generates a param converter service
service:path-processor (path-processor) Generates a path processor service
service:request-policy (request-policy) Generates a request policy service
service:response-policy (response-policy) Generates a response policy service
service:route-subscriber (route-subscriber) Generates a route subscriber
service:theme-negotiator (theme-negotiator) Generates a theme negotiator
service:twig-extension (twig-extension) Generates Twig extension service
service:uninstall-validator (uninstall-validator) Generates a uninstall validator service
test:
test:browser (browser-test) Generates a browser based test
test:kernel (kernel-test) Generates a kernel based test
test:nightwatch (nightwatch-test) Generates a nightwatch test
test:unit (unit-test) Generates a unit test
test:webdriver (webdriver-test) Generates a test that supports JavaScript
theme:
theme Generates Drupal theme
theme:settings Generates Drupal theme-settings.php file
yml:
yml:breakpoints (breakpoints) Generates a breakpoints yml file
yml:links:action (action-links) Generates a links.action yml file
yml:links:contextual (contextual-links) Generates links.contextual yml file
yml:links:menu (menu-links) Generates a links.menu yml file
yml:links:task (task-links) Generates a links.task yml file
yml:migration (migration, migration.yml) Generates a migration yml file
yml:module-libraries (module-libraries) Generates module libraries yml file
yml:permissions (permissions, permissions.yml) Generates a permissions yml file
yml:routing (routing, routing.yml) Generates a routing yml file
yml:services (services, services.yml) Generates a services yml file
yml:theme-libraries (theme-libraries) Generates theme libraries yml file2. Para nuestro caso vamos a crear un módulo que use una interface ThemeNegotiatorInterface para poner un theme sólo en una página en especifico, esto lo haremos utilizando la opción module mencionada en esta lista dentro de la sección _global:
(Para entender como a detalle como trabajar con ThemeNegotiatorInterface puede ver este enlace https://softwinperu.com/drupal-developer/blog/usando-themenegotiator-para-cambiar-de-theme-por-codigo-en-drupal-8-9-y-10).
$ ./vendor/bin/drush generate module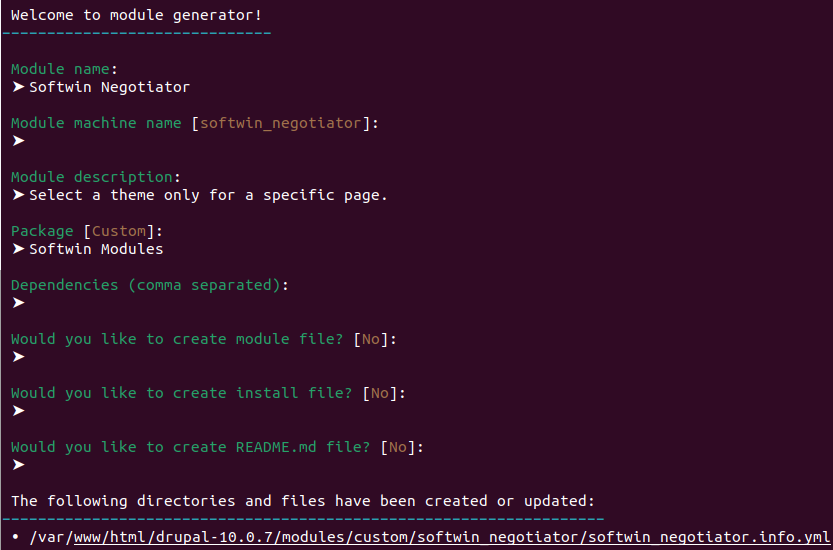
3. Con esto, en nuestra estructura de carpetas se habrá creado modules/custom/softwin_negotiator/softwin_negotiator.info.yml y en dicho archivo tendremos el código con la información de nuestro módulo:
name: 'Softwin Negotiator'
type: module
description: 'Select a theme only for a specific page.'
package: Softwin Modules
core_version_requirement: ^104. Ahora crearemos la página sobre la que luego trabajaremos, para ello utilizaremos la opción controller de la lista que vimos dentro de la sección _global:
$ ./vendor/bin/drush generate controller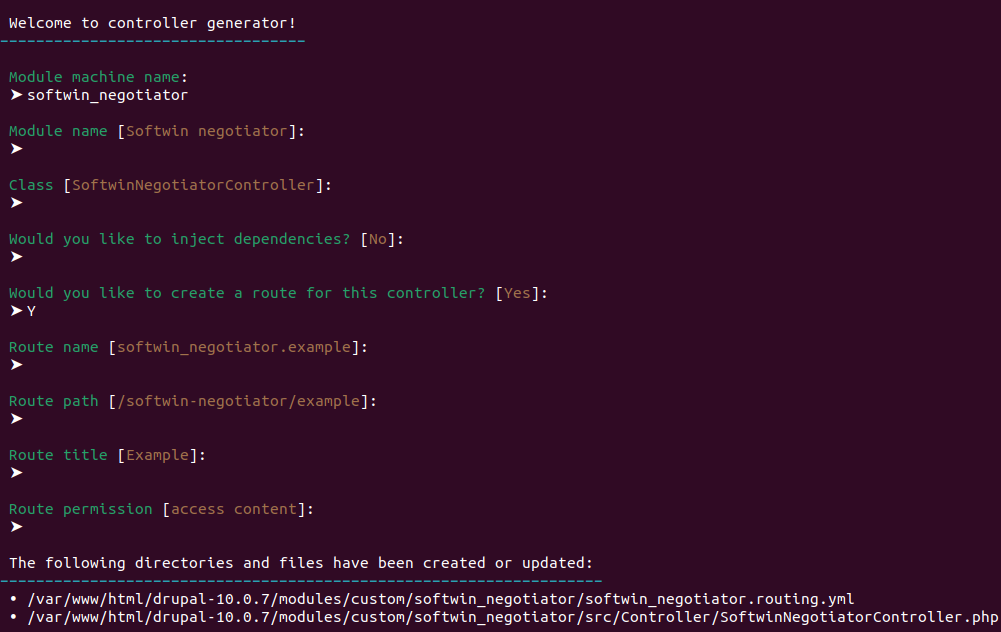
5. Como vemos, también nos preguntó el machine name del módulo sobre el que haremos este cambio y si deseamos un route para este controller. Además en la parte inferior de esta última imagen nos confirma que se crearon 2 nuevos archivos:
modules/custom/softwin_negotiator/src/Controller/SoftwinNegotiatorController.php
<?php declare(strict_types = 1);
namespace Drupal\softwin_negotiator\Controller;
use Drupal\Core\Controller\ControllerBase;
/**
* Returns responses for Softwin negotiator routes.
*/
final class SoftwinNegotiatorController extends ControllerBase {
/**
* Builds the response.
*/
public function __invoke(): array {
$build['content'] = [
'#type' => 'item',
'#markup' => $this->t('It works!'),
];
return $build;
}
}
modules/custom/softwin_negotiator/softwin_negotiator.routing.yml
softwin_negotiator.example:
path: '/softwin-negotiator/example'
defaults:
_title: 'Example'
_controller: '\Drupal\softwin_negotiator\Controller\SoftwinNegotiatorController'
requirements:
_permission: 'access content'
Hasta aquí tenemos la página lista con su respectivo controller y routing.
Asignando un theme a una página especifica
Tenemos muchos usos adicionales para Drush, y son los que vemos en la lista al inicio, como crear un formulario, un bloque o un servicio. Para nuestro ejemplo crearemos un servicio.
Ahora pasaremos a crear la clase que se encargará de asignar un tema distinto sólo a esta nueva ruta, esta clase debe implementar la interface ThemeNegotiatorInterface.
Para crear dicha clase (que es será un servicio) usaremos la opción service:theme-negotiator vista en nuestra lista en la sección service.
$ ./vendor/bin/drush generate service:theme-negotiator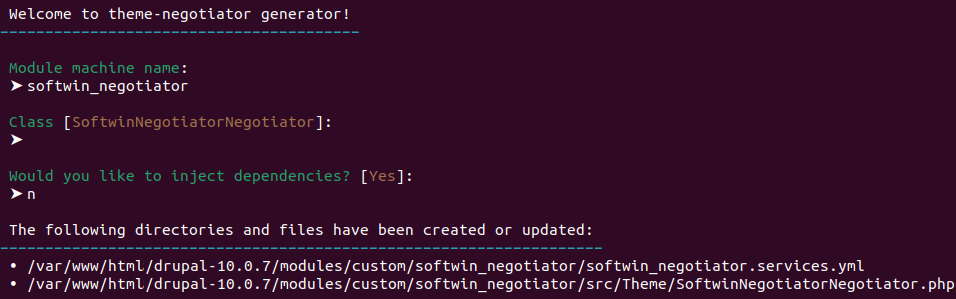
Como vemos, también nos preguntó el machine name del módulo sobre el que haremos este cambio y si deseamos inyectar dependencias. Además en la parte inferior de esta última imagen nos confirma que se crearon 2 nuevos archivos:
modules/custom/softwin_negotiator/softwin_negotiator.services.yml
services:
theme.negotiator.softwin_negotiator.example:
class: Drupal\softwin_negotiator\Theme\SoftwinNegotiatorNegotiator
arguments: ['@request_stack']
tags:
- { name: theme_negotiator, priority: 1000 }
modules/custom/softwin_negotiator/src/Theme/SoftwinNegotiatorNegotiator.php
<?php declare(strict_types = 1);
namespace Drupal\softwin_negotiator\Theme;
use Drupal\Core\Routing\RouteMatchInterface;
use Drupal\Core\Theme\ThemeNegotiatorInterface;
/**
* Defines a theme negotiator that deals with the active theme on example page.
*/
final class SoftwinNegotiatorNegotiator implements ThemeNegotiatorInterface {
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function applies(RouteMatchInterface $route_match): bool {
return $route_match->getRouteName() === 'softwin_negotiator.example';
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function determineActiveTheme(RouteMatchInterface $route_match): ?string {
// @DCG Here you can determine the active theme for the request.
return 'claro';
}
}
- Vemos que por defecto tomó softwin_negotiator.example como el routing, pero podríamos cambiarlo si lo deseamos y lo mismo en cuarquier parte del código generado.
- Además este código nos dice que cuando se use el routing softwin_negotiator.example, entonces se retornará el theme claro, el cual también podríamos cambiar si queremos.
Me pareció interesante el artículo


Añadir nuevo comentario